Core Concepts
Understanding the fundamental building blocks of NodeMatrix
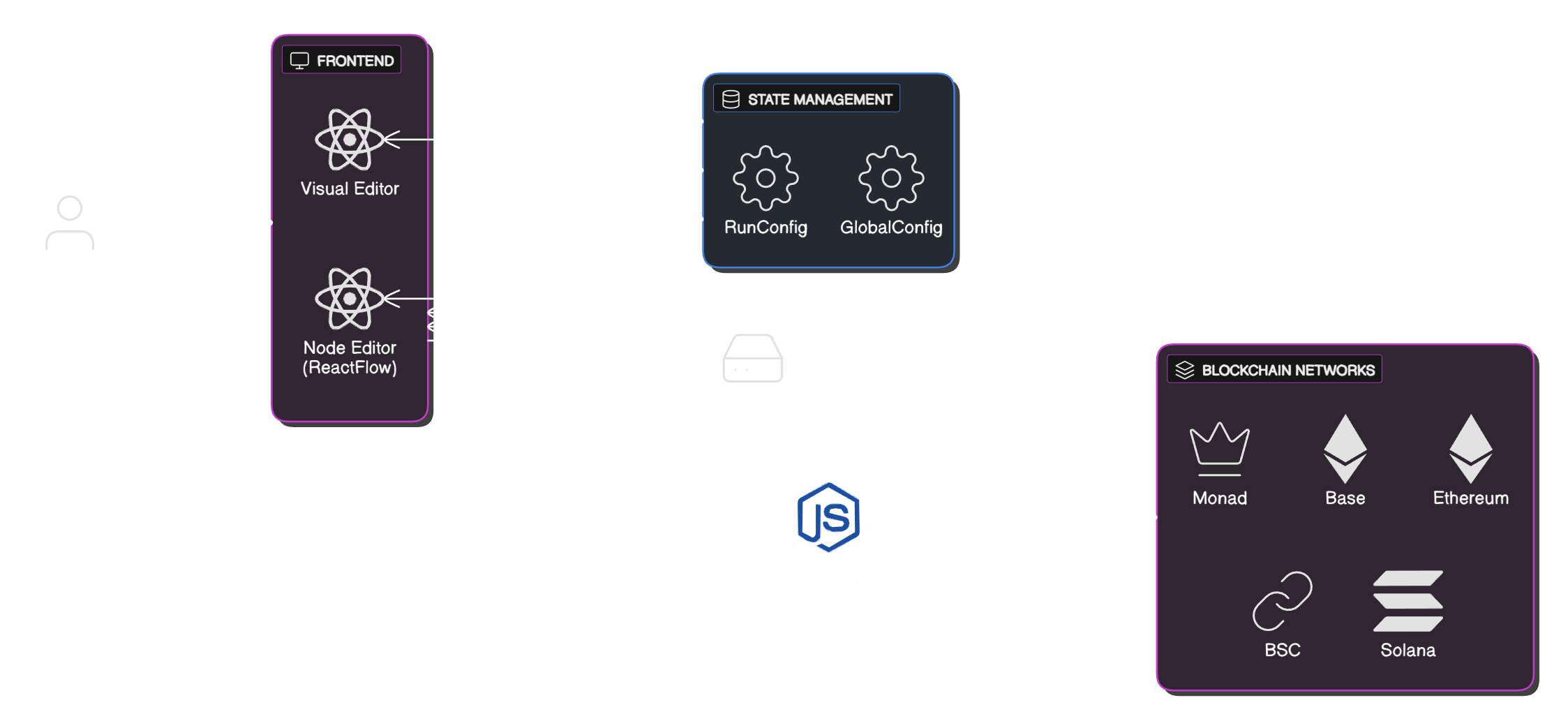
Three-Layer Architecture
NodeMatrix is built on a robust three-layer architecture that separates concerns and ensures security:
Frontend Layer
React-based visual editor where you build workflows. Runs entirely in your browser for maximum security.
Backend Layer
Node.js execution engine that monitors triggers and executes workflows according to your configuration.
Blockchain Layer
Smart contracts on EVM chains store your workflow configs and execute on-chain operations.
What are Nodes?
Nodes are the fundamental building blocks of NodeMatrix. Each node represents a specific action or condition in your automation workflow. Think of nodes as LEGO blocks - you connect them together to build complex automations.
Trigger Nodes
Start your workflow based on events like price changes, time intervals, or on-chain events.
Action Nodes
Execute operations like token swaps, transfers, contract calls, or social media posts.
Logic Nodes
Add conditions, loops, and branching logic to create intelligent workflows.
Data Nodes
Fetch, transform, and store data from APIs, oracles, and on-chain sources.
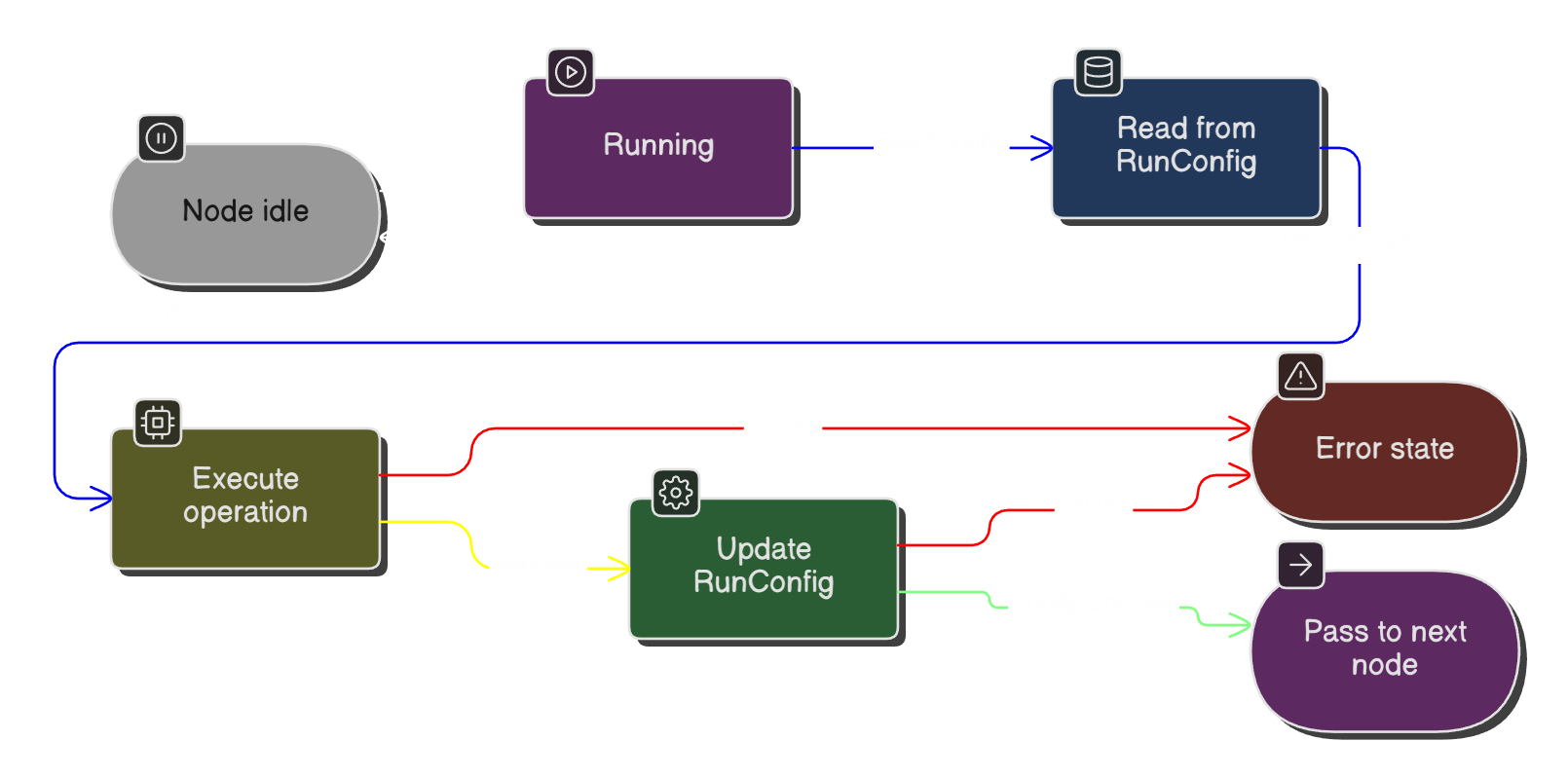
The Node Execution Lifecycle
Every node in NodeMatrix follows a predictable four-step execution cycle. Understanding this cycle is key to building reliable automations:
- 1
READ State
Node retrieves current state from the blockchain or external data sources
- 2
EXECUTE Logic
Node performs its configured operation (swap, transfer, call, etc.)
- 3
UPDATE State
Node saves results and updates on-chain state if necessary
- 4
PASS to Next
Node forwards output data to connected downstream nodes
Workflows
A workflow is a collection of connected nodes that work together to accomplish a task. Workflows can be simple (two nodes) or complex (dozens of interconnected nodes with branching logic).
Workflow Execution
Connections
Connections are the lines that link nodes together. Data flows through these connections from output ports to input ports. Each connection type carries specific data formats.
Connection Types
- Data Connections (Green)
Pass structured data like token amounts, addresses, or API responses.
- Flow Connections (Blue)
Control execution order and trigger subsequent nodes.
- Event Connections (Purple)
React to on-chain events, webhooks, or external triggers.
State Management
NodeMatrix maintains state across workflow executions, allowing you to build stateful automations that remember previous runs and make decisions based on historical data.
Persistent Storage
Store variables, counters, and data that persist between workflow runs.
Encrypted State
Sensitive data is encrypted at rest using your wallet's public key.
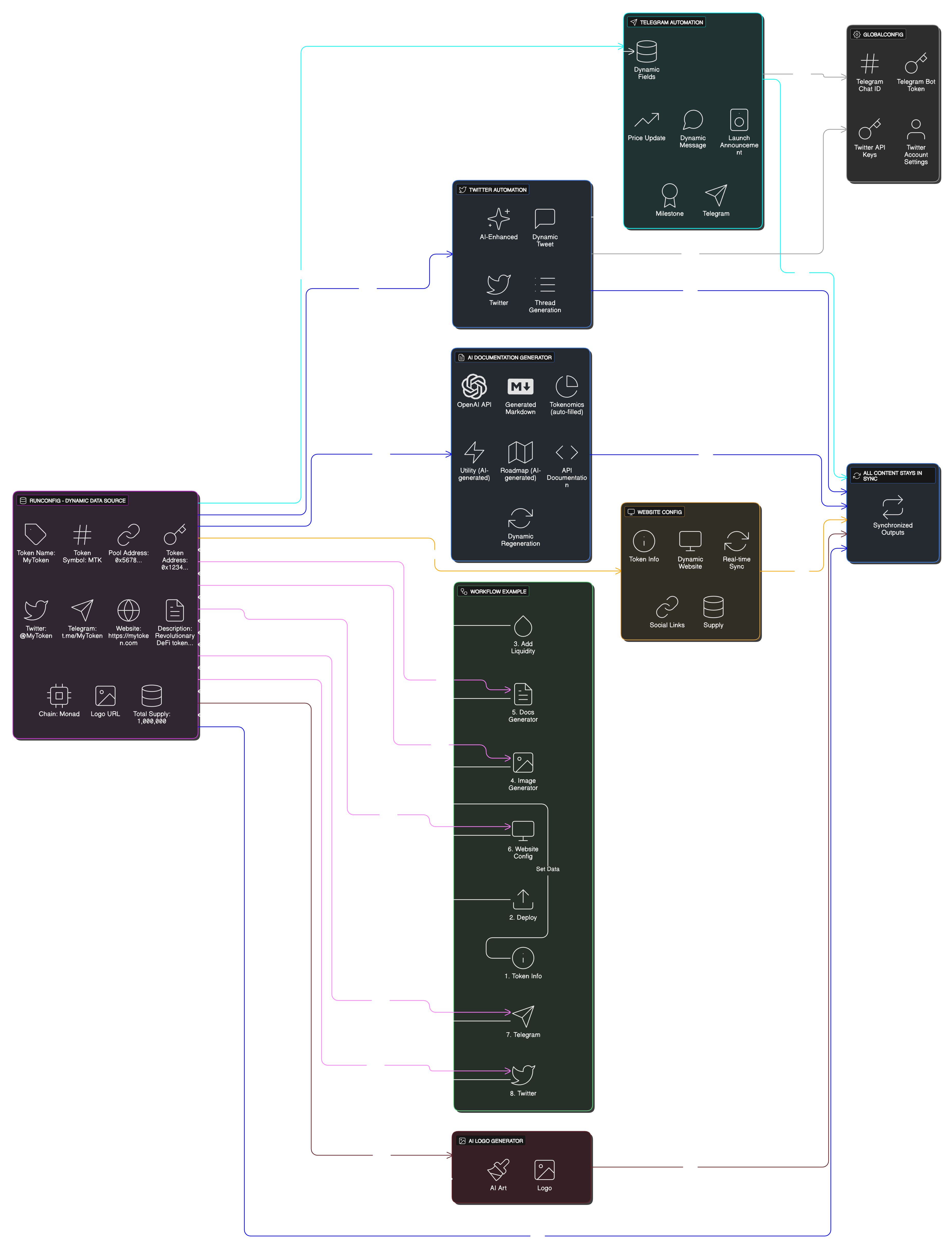
Putting It All Together
This comprehensive diagram shows how all NodeMatrix components work together in production. The RunConfig system manages your workflow configurations on-chain, while the execution engine monitors triggers and coordinates node execution across multiple chains.
Notice how state flows bidirectionally - nodes can read from and write to shared state, enabling complex stateful automations that remember previous executions and adapt their behavior over time.